177Lu-PSMA radionuclide therapy
What is 177Lu-PSMA therapy?
PSMA radionuclide therapy with Lutetium 177 (177Lu) for prostate cancer is a targeted radiation treatment for prostate cancer that uses PSMA enzymes on the surface of cancerous cells to deliver the radiopharmaceuticals and destroy the tumor and metastases directly with minimal damage to the surrounding healthy tissue.
Prostate cancer cells contain an enzyme called prostate-specific membrane antigen or PSMA. In almost all cases this enzyme is very abundant on the surface of both the primary tumor and its metastases. This fact is used by medicine both for diagnostics and for treatment. Hence the blend name of this medical field - theranostics, i.e. the combination of therapy and diagnostics of the target.
How does the treatment work?
The so-called biomarkers or ligands, i.e. substances that dock to the surface markers, are loaded with nuclides or radioactive substances. For the PSMA radionuclide therapy, ligands are labelled with radioactive substances lutetium-177 (beta emitter) or actinium-225 (alpha emitter). Radioligands are injected intravenously, thereafter they attach to cancer cells and the emitters begin to destroy them. The fact that the radiation radius of lutetium and actinium is very localized (lutetium does not penetrate the surrounding tissues deeper than 1-2 mm, and actinium - deeper than 1-2 cell diameter) significantly reduces the collateral damage that often accompanies traditional radiation treatment.
The doctor will decide which emitter, in what quantity or in which combination to use depending on your specific case.
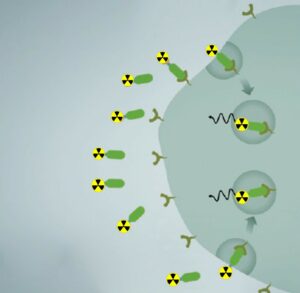
Labelled radioligands dock to PSMA
Procedure
The procedure itself takes about 15-20 minutes. Radioligands are intravenously administered to the patient. For supportive purposes, in order to lessen the strain on kidneys, you should drink plenty of fluids before and after therapy. You can leave the clinic immediately after the therapy. We will inform you in detail in advance as to the specific radiation precautions.
The usual initial treatment course consists of 3 sessions with a 4-week interval in-between accompanied by a 68Ga PSMA-PET/CT in 6-7 weeks after the third session to evaluate the efficacy. Further treatments afterwards are possible.
In the following days
It is recommended to drink as much fluids as possible (appr. 2.5–3 litres) in order to accelerate the excretion of radioactive substances, and to avoid excessive physical exercise where possible. You might experience slight fatigue in the next 2-3 days. Out of abundance of caution, try to avoid contact with pregnant women and small children in the next 3 days. Then again, you do not pose any danger to people in your household.
Positive effects
Particularly for prostate cancer, extensive data are already available demonstrating the successful application of this therapy in advanced, metastasized stages of disease.
It was shown that a therapeutic response was achieved in more than 80% of patients in this group of patients. In general, the intravenous administration of PSMA targeting radioligands is very well tolerated and this type of therapy can be repeatedly applied.
Possible side-effects
Both salivary glands and kidneys possess the PSMA enzyme too. However, severe side effects in these organs have not been observed in thousands of treatments. To a low extent and mostly only after repeated treatment, xerostomia or dryness of the mouth is the most frequently reported side effect (usually temporary).
In patients with preexisting bone marrow damage and multiple bone metastases a mostly reversible alteration in blood count was described. The findings of the VISION trial presented in March 2021 demonstrated that overall the 177Lu-PSMA-617 therapy is well tolerated. For further information please consult “Lutetium-177–PSMA-617 for Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer”.
For medical professionals
The term „PSMA therapy“ comprises all applications of highly specific radioligands selectively targeting a protein on the cell surface, called PSMA. Since this molecular target was first detected on prostate cancer cells, it was given the name “prostate specific membrane antigen”, or abbreviated “PSMA”. The name is somewhat misleading since newer findings show that this protein also displays enzymatic functionality. It is therefore also known as folate hydrolase.
If this protein is overexpressed on tumor cells, an activation of a tumor cascade is triggered which subsequently leads to aggressive proliferation and metastatic infiltration. Latest findings show that also tumors other than prostate cancer express this enzyme on their cell membranes. Radioligand therapy using highly specific PSMA-targeting molecules (through the incorporation of a chemical urea-based moiety that binds to this protein) enables to apply this technique also in these tumors by pinpointing and destroying the respective tumor tissue. Since the mass of used substances is minuscule and the therapeutic effect is solely resulting from the delivered radiation energy directly within the target tissue, side effects are only expectable to a very low extent. In PSMA therapy, the beta-radiation emitting nuclide lutetium-177 (177Lu; half-life 6.7 days) is currently used most prominently which delivers almost all its energy within 1 to 2 mm in tissue. By inducing both apoptosis and direct cell damage, radioligand therapy produces both immediate and delayed therapeutic effects. In some cases, this can even take a few months after completing the therapy.
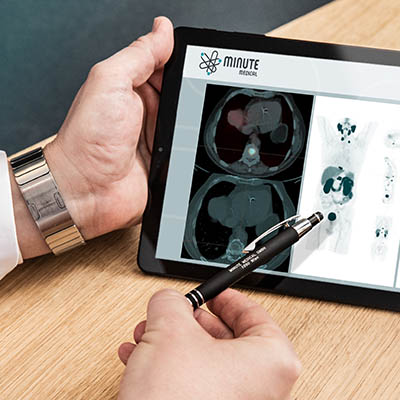

As for all therapies in nuclear medicine the theragnostic potential of the used radioligands can be exploited by verifying the increased expression of the target protein within tumor tissue by specific PSMA PET-imaging before 177Lu-PSMA therapy.


Therapy planning


For this purpose, the identical molecular target, i.e. the PSMA protein, is accessed using a molecule incorporating the same binding motif and a diagnostic radionuclide (e.g. 68Ga) for signaling in positron emission tomography (PET scanning).





The evaluation of your molecular imaging data enables us to decide whether you are eligible for PSMA radionuclide therapy. In addition, we conduct an interdisciplinary review of your specific situation to derive your individual and personalized concept.
For further information and your individual therapy planning, please contact us directly.